Arsenic is a toxic chemical element that can be found in natural deposits in the earth’s crust. When groundwater comes into contact with these deposits, then it dissolve and accumulate arsenic, resulting in arsenic contamination in drinking water. The presence of arsenic in groundwater is a serious public health concern, Arsenic can lead to a […]
Read MoreCategory: Ground Water Hydrology
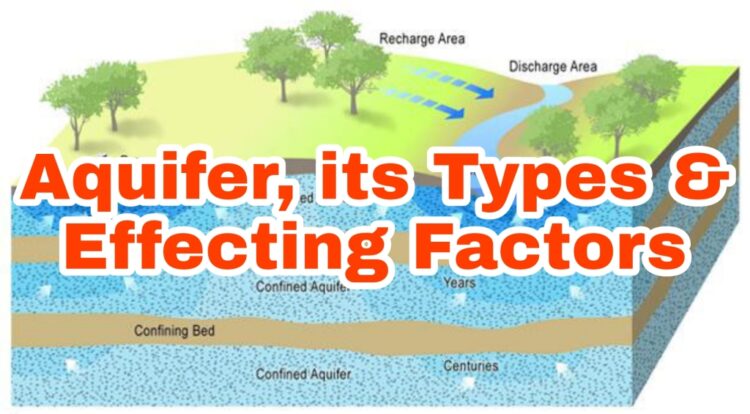
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock, sediment, or soil. Aquifers can store large amounts of water and are a major source of groundwater for drinking, irrigation, and other uses. Aquifers are recharged by precipitation, surface water, and other sources of water. Groundwater from aquifers is often the only source of water […]
Read More
Seven Ways to Make Groundwater more Visible are given below 1: Demystifying 2: Understanding the complexity 3: Data on Hidden use 4: Unlocking Potential 5: Seeing the impact of climate change 6: Highlighting its role for Biodiversity 7: Joining Hands
Read More
Acute arsenic exposure (i.e. high concentration about 1650ug/l ingested during short period of time) can cause a variety of adverse effects. Acute high dose oral exposure to arsenic typically leads to gastrointestinal irritation accompanied by difficulty in swallowing, thirst, and abnormally low blood pressure. Death may also occur from cardiovascular collapse. Chronic arsenic uptake may […]
Read More
Fluoride contamination in the groundwater has got great attention in last few decades due to their toxicity. Fluoride when ingested in small quantities (<0.5 mg/L) is beneficial in promoting dental health by reducing dental caries, whereas higher concentrations (>1.5 mg/L) may cause fluorosis. It is estimated that about 200 million people, from among 25 nations […]
Read More
Humans are usually exposed to arsenic compounds primarily through contaminated air, food, and water sources. The consumption of contaminated water for drinking is also an important source of arsenic exposure. Generally concentration of arsenic is usually higher in ground water than in surface water, especially when and where specific geochemical conditions favor dissolution of arsenic […]
Read More
The contamination of As can be propagated defectively into the groundwater system because As in groundwater and aquifers is mobilized (e.g., hydraulic fracturing). Hence, its contamination can affect a large population of people. Groundwater concentration of As has been documented in the literature which reveals a very large range from less than 0.5 to 5000 ppb […]
Read More







